The POY filament production line is a crucial link in the polyester chemical fiber industry. It is the complete process of processing polyester melt or chips into pre-oriented filaments. POY stands for Pre-Oriented Yarn, which means pre-oriented filament. Its molecular chain already has a certain degree of orientation, but its crystallinity is very low and it does not have the strength for direct textile use. It is mainly used in subsequent texturing (to produce DTY) or stretching (to produce FDY) processes.
I. Overview of POY Production Line
POY production line is a highly automated and continuous chemical fiber spinning system. The core objective is to stably produce POY filament cakes with uniform strips and consistent physical properties from high-viscosity polyester melts through precise spinning, cooling, oiling, winding and other processes.
Ii. Main Process Flow and Equipment
A complete POY production line usually includes the following key sections:
1. Raw material supply and melting system
• Raw materials: Mainly polyester melt (directly conveyed from the polymerization unit pipeline, with the lowest cost) or solid polyester chips (requiring remelting).
• Main equipment:
Slice drying system (if slicing is used) : Remove moisture from the slices to prevent hydrolysis at high temperatures from causing a decrease in molecular weight. Drum drying or air flow drying is usually adopted.
Screw extruder (if slicing is used) : Core melting equipment. The slices are conveyed, compressed, melted and homogenized in the screw, and are transformed into uniform, constant-temperature and constant-pressure melts.
Melt filter: It removes impurities such as gel particles and carbonized particles from the melt to ensure that the spinning assembly and spinneret are not clogged, which is crucial for product quality.
Melt conveying pipeline and metering pump: Precisely and stably convey clean melt to each spinning position. The metering pump (gear pump) ensures that the amount of melt discharged at each spinning position is absolutely precise, which is the key to controlling the fineness of the filament.
2. Spinning and cooling forming system
• Spinning box and components:
The melt enters the spinning box and reaches each spinning position through the distribution pipeline.
The spinning assembly is the core component, which is equipped with fine filtering materials (such as sea sand and metal mesh) and spinnerets inside. There are a large number of micron-sized precision holes on the spinneret, and the melt is extruded under high pressure to form multiple fine streams.
• Side-blowing air cooling system:
The fine stream of high-temperature melt extruded from the spinneret meets the clean air that has undergone constant temperature, humidity and wind speed perpendicularly in the side-blowing air window, and rapidly cools and solidifies into filaments.
The uniformity and stability of the O-side blowing air directly determine the internal structure of the filament and the uniformity of the filament shaft.
3. Filament bundling, oiling and traction system
• Bundling (guide wires) : After cooling, multiple single wires are guided into a bundle by a guide wire to prevent them from adhering to each other.
• Oiling: The filament bundle is evenly coated with spinning oil through the loading machine or oiling nozzle. The role of oiling agents is of vital importance: lubrication (reducing friction and preventing fuzziness), antistatic, and clamping (preventing single filaments from bundling apart).
• First traction roller: Also known as “feeding roller” or “network roller”. It steadily leads the filament bundle out from the spinning end at a certain speed and transmits it to the winding machine. The difference between its speed and the winding speed determines the extent to which the filament is stretched, thereby controlling the pre-orientation degree of POY. Some devices will also add network devices here to create periodic entanglements between the single filaments and increase the clamping force.
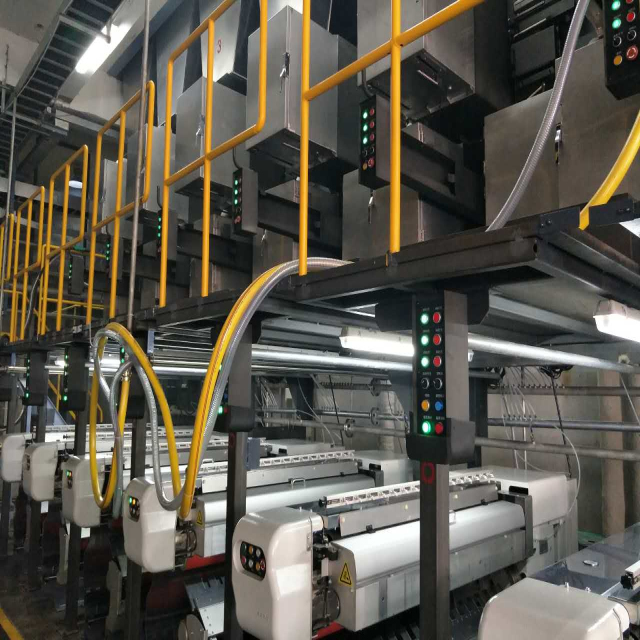
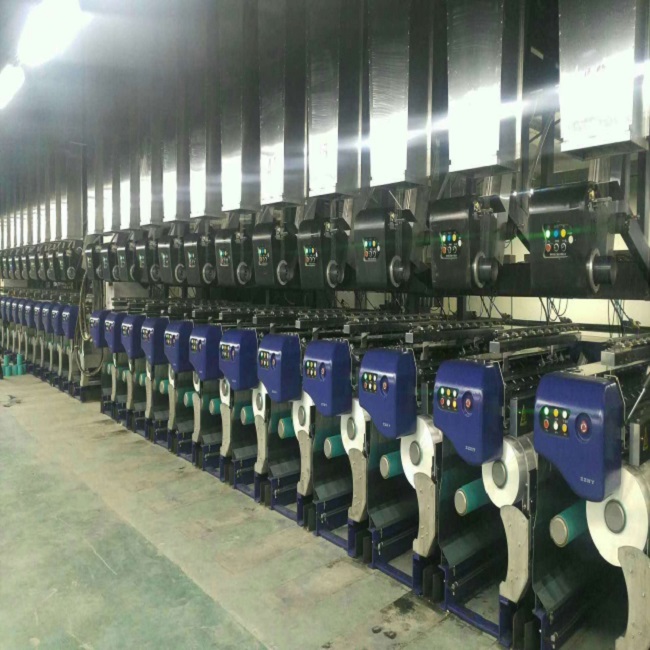
4. High-speed winding system
This is the terminal and high-speed core equipment of the production line.
• Second traction roller: In coordination with GR1, it precisely controls the stretching of the filament bundle.
• Winding head: At high speed, the filament is wound onto the paper tube in a specific winding manner (such as parallel winding or conical winding) to form a well-shaped POY filament cake.
Modern winding machines operate fully automatically and are equipped with functions such as automatic head raising, automatic barrel dropping, automatic barrel changing, and online quality monitoring (such as broken head and wire tripping detection).
Iii. Key Characteristics of POY Filament
• High orientation and low crystallization: Due to the tensile effect of high-speed winding, the molecular chains are arranged (oriented) along the fiber axis to a certain extent, but do not have sufficient time to form crystals.
• Lower strength and higher elongation: Compared with fully drawn wire (FDY), POY has lower strength and a higher elongation at break (usually >100%).
• Storage stability: The POY structure is unstable. During storage, “post-crystallization” may occur, causing performance changes over time. Therefore, it is not suitable for long-term storage and should be processed as soon as possible.
• Subsequent processability: It is a high-quality intermediate product for manufacturing stretched and deformed filaments (DTY, false twist deformation) and fully stretched filaments (FDY, one-step spinning and stretching method).
Iv. Technical Features of Modern POY Production Lines
High-speed operation: The winding speed is continuously increased to enhance production efficiency.
2. Large-scale: The number of spinneret holes at a single spinning position increases (such as multi-head spinning), and the daily output of a single production line can reach several hundred tons.
3. Automation and Intelligence
Full-process automatic control (DCS/PLC).
The robot automatically drops the cylinder, packages and stores.
Online quality monitoring system (such as dryness meter, oil agent detection).
Big data analysis enables process optimization and predictive maintenance.
4. Energy conservation and environmental protection
Adopt energy-saving screw and heat medium systems.
Waste gas recovery and waste heat utilization.
Low fuel consumption and oil recovery technology.
Post time: Jan-14-2026