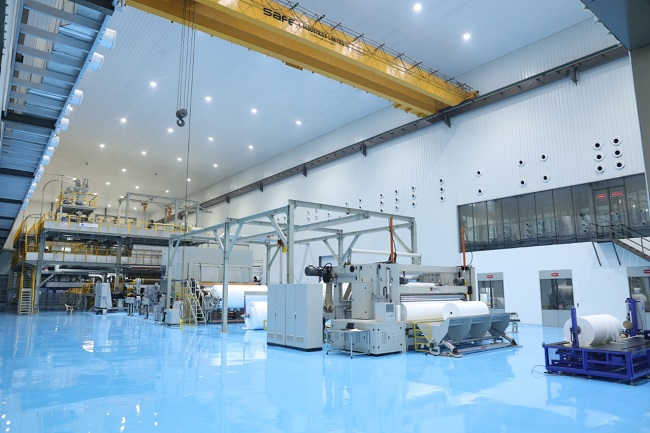
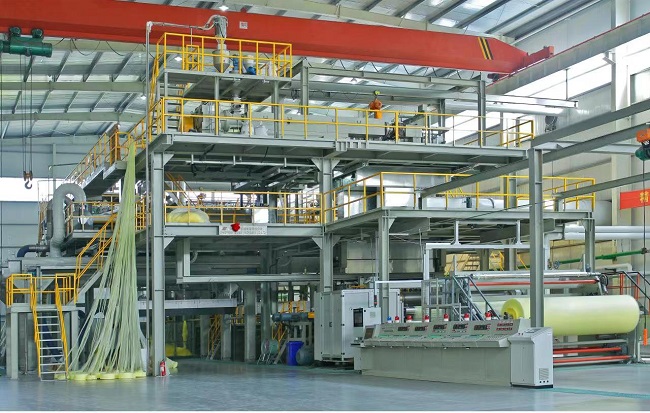
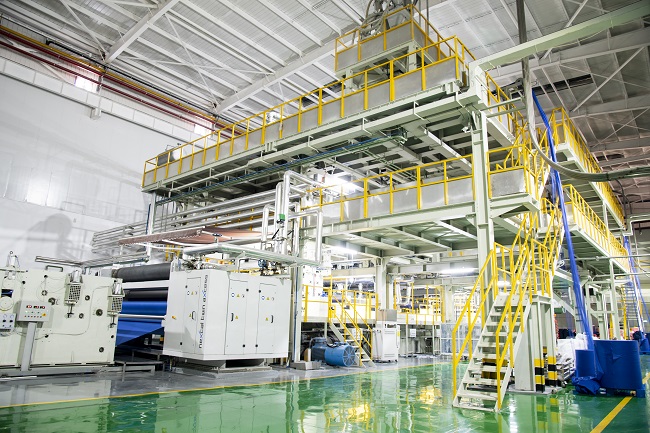
Today, with the rapid development of materials science and technology, spunbond nonwoven fabric, with its excellent performance and wide application, has become an indispensable core material in modern industry and daily life. CTMTC is committed to providing customers with globally leading full-process technology and equipment for spunbond nonwoven fabrics. It not only offers equipment but also helps customers build sustainable manufacturing capabilities and market competitiveness.
I. Detailed Explanation of the Technical Principle of Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
Spunbonding is one of the most important production processes for nonwoven fabrics. The core principle can be regarded as the combination of the spinning technology of chemical fiber filaments and the web-forming technology of nonwoven fabrics.
The basic process is as follows:
Raw materials and modification treatment: Commonly used polymer chips such as polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), nylon (PA), etc., can be modified through blending, adding functional masterbatches, and other methods to endow products with special properties such as antistatic, antibacterial, flame-retardant, and hydrophilic.
Multi-component spinning (advanced process is optional) : To produce superfine fibers or functional fibers, two-component or even multi-component spinning technology can be adopted. Using more than two sets of extrusion systems, different polymers (such as PET/PA, PP/PE) are extruded through specially designed composite spinning components to form composite filaments with cross-sectional structures such as “island type” and “split type”. Subsequently, through thermal bonding and processing, the composite fibers can be split or peeled off to obtain ultra-fine fiber webs at the micrometer or even nanometer scale, which is a key path to achieving high-end product development.
Melt extrusion: Polymer chips are heated and melted in a screw extruder to become a melt.
Filtration metering: The melt passes through a filter to remove impurities, and the flow rate is precisely controlled by a metering pump and sent to the spinning assembly.
Spinning: The melt is extruded through a spinneret to form continuous filaments.
Cooling and drawing: A key process step. Fibers are stretched, cooled and refined through high-speed and high-temperature gas flow or mechanical stretching systems to promote molecular orientation and crystallization and enhance fiber strength.
Web formation: After stretching, the long filaments are evenly and randomly laid on the web-forming curtain under negative pressure to form a fiber web. This is the prototype of the nonwoven fabric “cloth”.
Reinforcement: By means of a hot rolling mill (thermal bonding) or a needling machine (mechanical reinforcement), the fibers in the fiber web are bonded together to obtain strength and form fabric.
Winding and post-treatment: After the fabric is made, it is slit and wound into rolls, or post-treatment such as anti-static, hydrophilic, and printing is carried out as required.
Ii. Detailed Explanation of Core Equipment on the Production Line
A complete spunbond production line is a highly integrated systems engineering project. The main equipment includes:
Raw material processing and feeding system
Equipment: including silos, vacuum feeders, drying systems, etc., to ensure that raw materials are clean, dry and stably conveyed.
Function: To ensure the clean, dry, continuous and stable supply of raw materials.
2. Extrusion and melting system
Core equipment: Screw extruder.
Detailed explanation: Multi-zone heating is used to plasticize solid slices into a uniform melt. Screw design (length-to-diameter ratio, compression ratio) is crucial to melt quality and output.
3. Spinning and drawing system
Core equipment: spinning box, metering pump, spinning assembly, drawing system.
Detailed explanation
Spinning assembly: It contains a precision filter and a spinneret. The spinneret can have up to several thousand holes, and the hole diameter determines the fineness of the fiber.
Stretching system: This is the key to distinguishing technical schools.
Tubular air flow drawing: High-speed air flow accelerates and stretches the fibers in a gradually shrinking drawing tube. The structure is relatively simple and it is widely applied.
Wide slit air flow stretching: The air flow is evenly ejected from the wide slit, making the stretching more uniform. It is suitable for producing ultra-fine denier and highly uniform products. The technical threshold is even higher.
Mechanical roller stretching: used for some special or high-strength products.
4. Network formation and reinforcement system
Web-forming equipment: web-forming machine (with suction device). High-speed spinning devices or direct use of air flow diffusion make the fibers randomly, disorderly and evenly spread out in the web. The speed and uniformity of the mesh curtain determine the uniformity of the gram weight.
Reinforcement equipment
Hot rolling mill: The most commonly used. The fibers are locally melted and bonded by a pair of heated steel rollers (one of which usually has pattern points) under temperature and pressure. The pattern design affects the softness, strength and appearance of the fabric.
Needling machine: It is used for the production of thicker and looser geotextiles and other products.
5. Winding and post-processing system
Winding machine: Automatic roll changing to ensure smooth winding and constant tension.
Post-processing line: It can be used for online lamination (such as SMS), coating, printing, corona treatment (to improve hydrophilicity), etc.
6. Control system
Core: Integrated DCS/PLC control system. It realizes real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment of thousands of parameters such as temperature, pressure, speed and gram weight, and is the “brain” of production stability and quality.
Iii. Analysis of Application Prospects
Spunbond nonwoven fabric, due to its high strength, high productivity, relatively low cost and wide range of adjustable performance, has a very broad application prospect and is constantly developing towards high-end and functional.
1. Traditional and pillar application areas (Stable growth)
Sanitary materials: Surface layer, drainage layer and bottom layer of disposable diapers, sanitary napkins and wet wipes. This is the largest market for spunbond fabrics, with rigid demand that continues to grow along with the upgrading of consumption.
Medical protection: surgical gowns, surgical hole sheets, isolation suits, protective suits, outer and inner layers of masks. After the pandemic, global awareness of protection has increased, and the demand for high-quality medical fabrics has become regular.
Packaging materials: shopping bags, file bags, laminated base materials, etc. Thanks to the “plastic restriction order”, the demand for eco-friendly packaging has soared.
2. Emerging and high-growth application fields (with huge potential)
Agriculture and Horticulture: Harvest cloth, weeding cloth, plant protection cloth, promoting the development of precision agriculture.
Geotechnical Engineering and architecture: roadbed reinforcement, drainage, roof waterproofing base materials, etc. Infrastructure construction and the development of “sponge cities” have brought about continuous demand.
Automotive industry: interior materials, carpet base fabrics, sound and heat insulation materials, air/oil filters. The trend of automotive lightweighting and environmental protection benefits nonwoven materials.
Filtration and separation: High-end fields such as air filtration (HVAC, industrial dust removal) and liquid filtration (water treatment, food industry). The fabric is required to have properties such as ultra-fine fibers, gradient structure, and chemical resistance, and it is a high value-added product direction.
Wiping and cleaning: Industrial wiping cloths, household cleaning cloths, with a high degree of market segmentation.
3. Future technologies and development trends
Ultra-fine and functionalized: The production of finer fibers is a key trend. Multi-component spinning technology (such as island type and split type) is the core process for achieving this goal. Through this technology, microfiber nonwoven fabrics can be produced in one step, significantly enhancing the softness, filtration performance, appearance texture and added value of the products. Meanwhile, through the combined design of polymers, it is easy to endow materials with specific functions such as hydrophilicity, hydrophobicity, flame retardancy and antibacterial properties.
Online lamination and integration: SMS (spunbond – meltblown – spunbond) remains the mainstream, but it has developed into more flexible multi-die head online lamination (such as SMMS, SSMMS), and one-step production of multifunctional composite materials.
Sustainability and Environmental Protection
Use degradable raw materials: such as PLA (polylactic acid) spunbond fabric.
Production energy conservation and emission reduction: Equipment is developing towards higher efficiency and lower energy consumption (such as low-temperature hot rolling).
Product recycling: Design to enhance the recyclability of fabric.
Intelligence and digitalization: The production line integrates more sensors and AI algorithms to achieve predictive maintenance, real-time closed-loop quality control, and digital twins, significantly enhancing efficiency and product consistency.
Personalized customization: Flexible production lines can meet the market demands for small batches, multiple varieties, and rapid switching.
If you are interested in CTMTC‘s business areas, cooperation models or service contents, and are eager to explore more cooperation possibilities, please feel free to contact us at any time!
Post time: Dec-17-2025